Air pollution is a critical issue that demands innovative solutions to mitigate its effects on human health and the environment. As the world grapples with this challenge, various Innovative Technologies to Combat Air Pollution effectively have emerged. This article explores some of the most promising technological advancements in the fight against air pollution, backed by research and real-world applications.
Table of Contents
Monitoring and Data Collection with Innovative Technologies to Combat Air Pollution
Advanced Air Quality Sensors and IoT Devices:
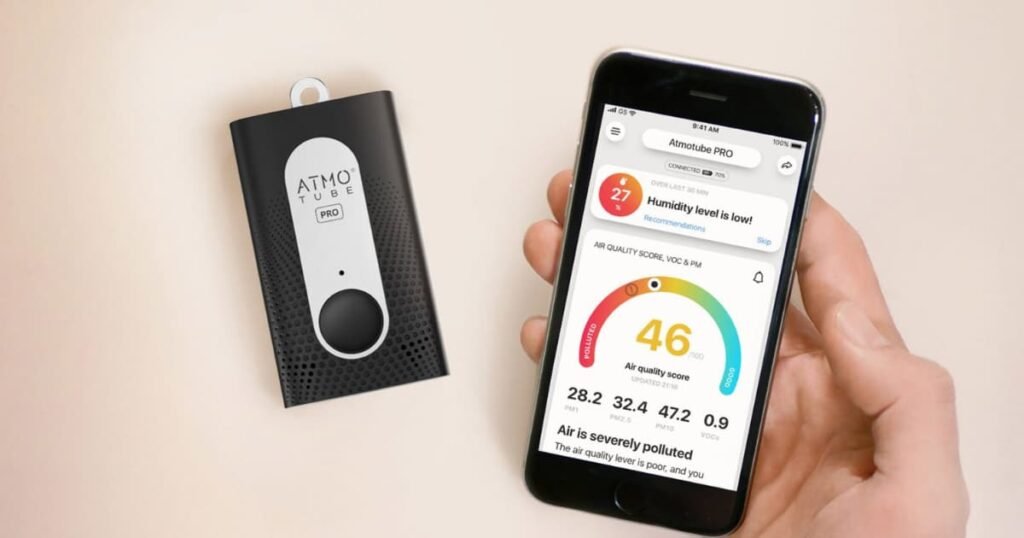
Smart Sensors are among the leading innovative technologies to combat air pollution, detecting and measuring pollutants like PM2.5, NO2, SO2, and O3 in real-time. These sensors, often connected via the Internet of Things (IoT), provide precise data on pollution levels, enabling timely responses. Wearable air quality monitors, such as TZOA and Atmotube, also offer personal air quality monitoring, alerting users to high pollution levels and suggesting protective measures.
Example: In Beijing, a network of smart sensors monitors air quality across the city, providing real-time data to the public and authorities. This system helps in making informed decisions about pollution control measures.

Pollution Control Technologies: Advanced Solutions
Air Purifiers:
HEPA and Activated Carbon Filters are widely used innovative technologies to combat air pollution by removing particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from indoor air. Modern air purifiers combine these technologies with smart features for enhanced performance. Electrostatic precipitators, which use electric charges to remove particles from the air, are commonly used in industrial settings to control emissions.
Example: The Dyson Pure Cool air purifier uses HEPA and activated carbon filters to capture pollutants and allergens, significantly improving indoor air quality.
Photocatalytic Oxidation:
Photocatalytic oxidation is another cutting-edge technology that combats air pollution. It uses ultraviolet light to activate a catalyst (usually titanium dioxide), which then breaks down pollutants into harmless substances like water and carbon dioxide. Photocatalytic coatings can be applied to buildings and surfaces to continuously clean the air by breaking down pollutants.
Example: The Palazzo Italia in Milan uses photocatalytic concrete to reduce air pollution, effectively turning the building into an air purifier.
Electrochemical Reduction:
This process involves using electricity to reduce pollutants into less harmful substances. It is particularly effective for removing nitrogen oxides (NOx) from industrial emissions. Electrochemical reduction showcases another form of innovative technology in the fight against air pollution.
Example: Researchers at the University of Illinois have developed an electrochemical cell that can reduce NOx emissions from power plants by over 90%.
Bioremediation:
Certain plants and algae can absorb and break down pollutants. Living walls and urban forests are examples of bioremediation techniques that improve air quality. These nature-based solutions are essential innovative technologies to combat air pollution.
Example: In Paris, the CityTree project uses panels filled with moss and other plants to filter pollutants from the air. Each CityTree can absorb up to 240 metric tons of CO2 annually.

Supporting Seaweed Farmers for Sustainable Packaging
Bhumi’s Commitment to Sustainable Agriculture
Here at Bhumi, we support seaweed farmers by integrating seaweed into the production of our biodegradable packaging. Seaweed farming is a sustainable practice that not only provides economic benefits to coastal communities but also contributes to environmental health by absorbing CO2 and reducing ocean acidification.
Seaweed in Biodegradable Packaging
Seaweed is a versatile raw material that can be processed into biodegradable packaging. We use seaweed as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics, helping to reduce plastic pollution and promote sustainability. By turning seaweed into packaging, we ensure that the material is biodegradable, reducing the environmental impact.
For more information about Bhumi’s sustainable practices, visit Bhumi Sustainable Agriculture.

Transportation Innovations to Combat Air Pollution
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles:
Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles are pivotal innovative technologies to combat air pollution, producing zero or reduced tailpipe emissions and significantly lowering urban air pollution. Advances in battery technology are making EVs more affordable and efficient.
Example: Tesla’s range of electric cars, such as the Model 3 and Model S, are leading the market with their long-range capabilities and high performance.
Public Transportation:
Transitioning to electric buses and trains can drastically reduce emissions from public transportation systems. Public transportation is a major area where innovative technologies to combat air pollution can make a significant impact.
Example: The city of Shenzhen in China has converted its entire bus fleet to electric vehicles, reducing CO2 emissions by 1.35 million tons annually.

Industrial Solutions to Reduce Emissions
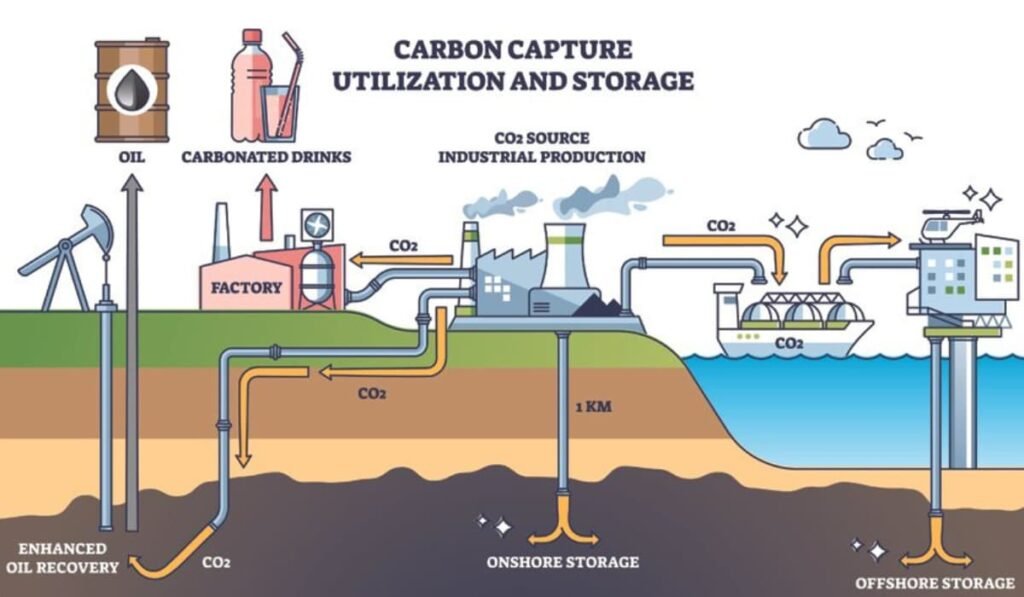
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
CCS technology captures carbon dioxide emissions from industrial sources and stores them underground, preventing them from entering the atmosphere. It is normally used in power plants, cement factories, and other industries with high CO2 emissions, representing one of the key industrial innovations to combat air pollution.
Example: The Boundary Dam Power Station in Canada uses CCS to capture and store CO2 emissions, significantly reducing its carbon footprint.
Scrubbers and Filters:
Wet Scrubbers: These devices remove pollutants from industrial exhaust gases by passing them through a liquid that absorbs the contaminants.
Baghouse Filters: These filters capture particulate matter from industrial emissions, preventing them from being released into the air.
Example: The use of wet scrubbers in coal-fired power plants in the United States has reduced sulfur dioxide emissions by over 90%.
Urban Planning and Design for Cleaner Air
Green Infrastructure:
Urban forests, green roofs, and other green infrastructure are effective innovative technologies to combat air pollution by absorbing pollutants and providing cooling effects.
Example: New York City’s MillionTreesNYC initiative aims to plant one million trees across the city, enhancing air quality and urban resilience.
Smart Cities:
Smart city initiatives use a combination of sensors, data analytics, and IoT to manage urban infrastructure and reduce pollution.
Example: Copenhagen’s smart city project includes a comprehensive network of sensors that monitor air quality, traffic, and energy use, helping the city achieve its goal of becoming carbon-neutral by 2025.

Conclusion
Innovative technologies to combat air pollution offer powerful tools, addressing the issue from multiple angles. From advanced air purifiers and electric vehicles to bioremediation and smart city planning, these solutions hold the promise of a cleaner, healthier future. For practical steps you can take to protect yourself from air pollution, read our post on How to Protect Yourself from Air Pollution. Additionally, explore real-world applications of these technologies in our post on Global Case Studies: Success in Air Quality Improvement.
References
- AirNow. (2021). Air Quality Index
- World Health Organization. (2020). Air pollution
- Chest Journal. (2019). The impact of short-term exposure to air pollution on health
- Lancet. (2018). Air pollution and stroke risk: A comprehensive review
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). (2013). Outdoor air pollution a leading environmental cause of cancer deaths
- Global Burden of Disease Study. (2019). Air pollution as a leading risk factor for premature death
By integrating these technologies and supporting policies that promote cleaner air, we can make significant strides in reducing air pollution and protecting public health.




