Deforestation not only devastates tree populations but profoundly affects soil health, leading to erosion, nutrient loss, and a decrease in biodiversity. This post delves into how deforestation catalyzes soil degradation and what can be done to mitigate its damaging impact.
Key Takeaways
- Soil erosion significantly increases due to tree removals.
- Nutrient depletion accelerates, stressing terrestrial ecosystems.
- Implemented sustainable practices can combat and reverse soil degradation.
- Biodiversity loss from deforestation affects microbial communities crucial for soil health.
- Global policy enforcement and local initiatives are vital for sustainable forestry management.
Table of Contents
- Impact of Deforestation on Soil Health
- Global and Regional Perspectives
- Innovative Solutions and Success Stories
- Policy Changes and Community Action
Impact of Deforestation on Soil Health
Deforestation is closely linked to the degradation of soil quality. The removal of forest cover not only leads to direct soil erosion but also disrupts the nutrient cycling crucial for long-term soil fertility.
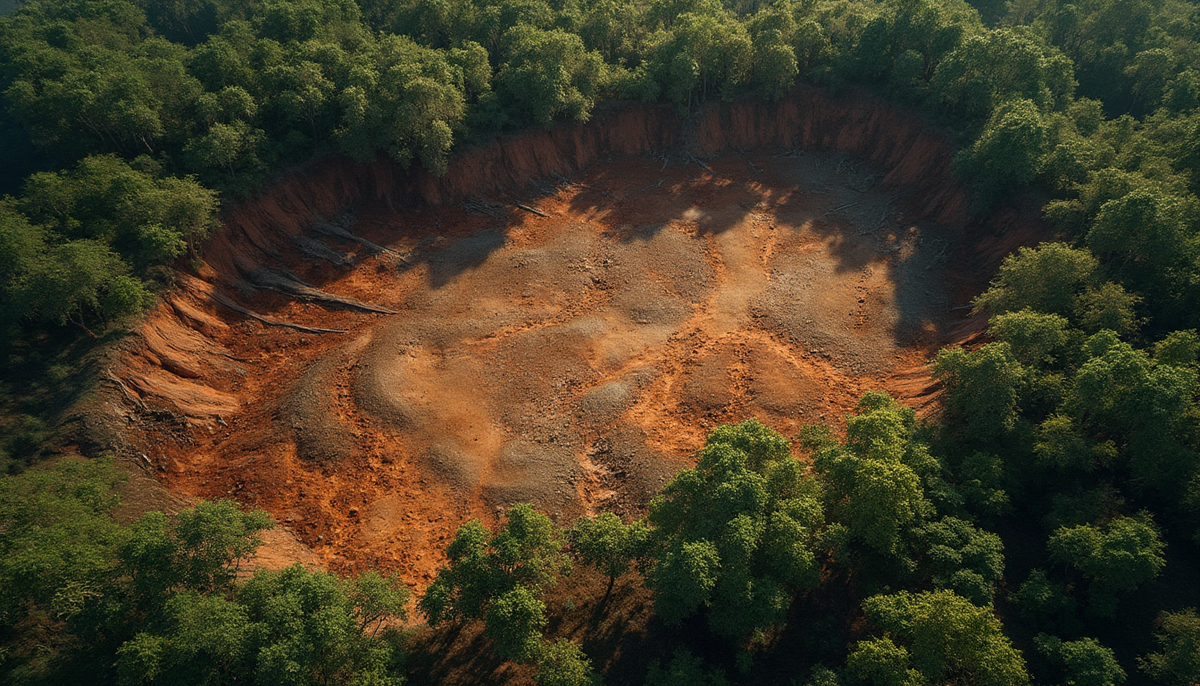

Emerging Challenges
Soil once protected under the canopy of forests becomes exposed and vulnerable. The direct impact of rain and the absence of root structures accelerate soil displacement, leading to sedimentation in rivers and loss of fertile top soil.
Global and Regional Perspectives
Deforestation affects soil health across the globe, with significant impacts in tropical regions where deforestation rates are highest. These areas suffer from severe soil erosion challenges impacting agricultural productivity and biodiversity.
Comparative Analysis of Policies
Countries approach the challenge differently, with varying degrees of success. For example, Brazil’s policy on Amazon rainforest conservation has seen varying levels of enforcement and success over the decades.
Innovative Solutions and Success Stories
Successful countermeasures against deforestation-induced soil degradation include sustainable forestry, agroforestry, and community-driven reforestation projects.

Agroforestry as a Sustainable Practice
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, enhancing biodiversity, reducing erosion, and improving water retention and carbon sequestration.
Policy Changes and Community Action
Policy development and community engagement are crucial in combating the adverse effects of deforestation on soil health. Strengthening environmental policies and fostering local initiatives can lead to more sustainable land management practices.
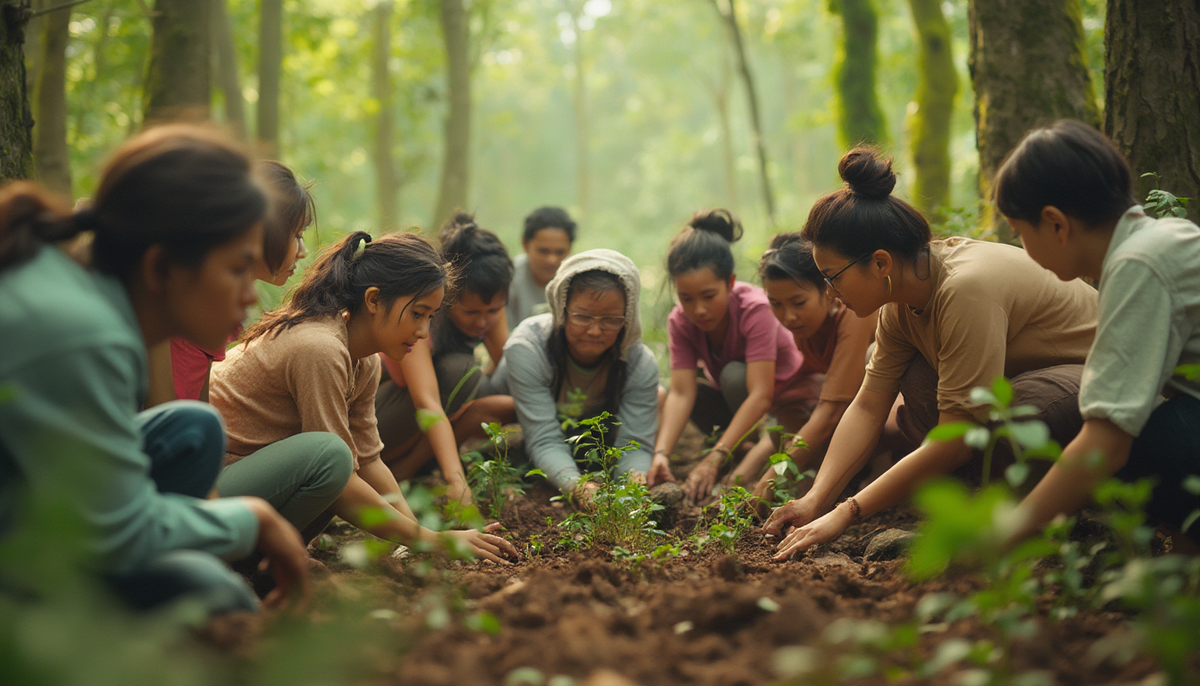

Community-led Conservation Initiatives
Grassroots movements often lead to sustainable practices that significantly impact soil conservation and forest preservation. Local efforts not only restore degraded lands but also foster a deeper connection between communities and their environment.
Conclusion
Addressing soil degradation from deforestation requires a multifaceted approach that includes global cooperation and local action. By understanding the extent of damage and implementing strategic interventions, we can work towards healthier ecosystems.
To learn more about the importance of soil health and sustainable practices, explore our articles on soil sustainability. Engage with us through donations or by joining our community efforts on Bhumi’s contact page.




